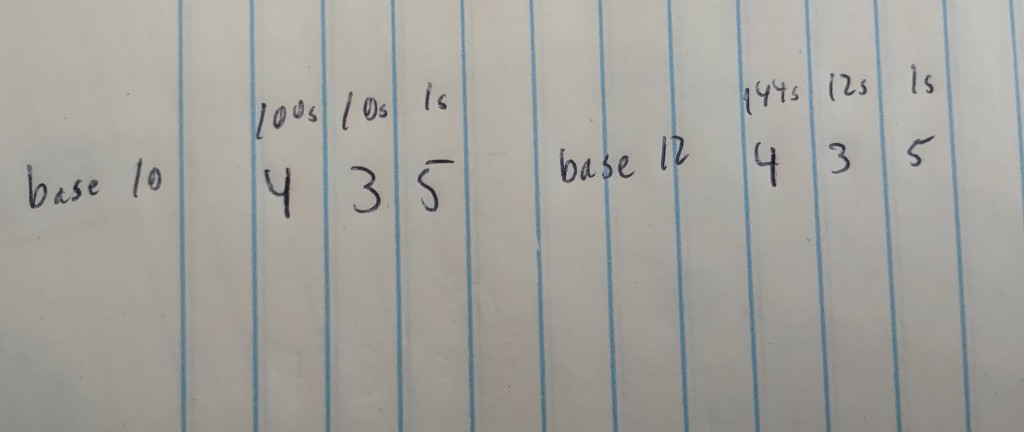It may surprise you to know, but I was once a philosopher. To be more accurate, I was once a clueless college student who thought “philosophy” would be a good major. I eventually switched to a science major, but not before I took more philosophy classes than most folks ever intend to.

A concept that was boring back then, but relavent now, is that of the “Chinese Room.” John Searle devised this thought experiment to prove that machines cannot actually think, even if they pass Turing Tests. The idea goes something like this:
Say we produce a computer program which takes in Chinese Language inputs and returns Chinese Language outputs, outputs which any speaker of Chinese can read and understand. These outputs would be logical responses to whatever inputs are given, such that the answers would pass a Turing Test if given in Chinese. Through these inputs and outputs, this computer can hold a conversation entirely in Chinese, and we might describe it as being “fluent” in Chinese, or even say it can “think” in Chinese.
But a computer program is fundamentally a series of mathematical operations, “ones and zeros” as we say. The Chinese characters which are taken in will be converted to binary numbers, and mathamatical operations will be performed on those numbers to create an output in binary numbers, which more operations will then turn from binary numbers back into Chinese characters.
The math and conversions done by the computer must be finite in scope, because no program can be infinite. So in theory all that math and conversions can themselves be written down as rules and functions in several (very long) books, such that any person can follow along and perform the operations themselves. So a person could use the rules and function in these books to: 1.) take in a series of Chinese characters, 2.) convert the Chinese to binary, 3.) perform mathamatical operations to create a binary output, and 4.) convert that binary output back into Chinese.
Now comes the “Chinese Room” experiment. Take John Searle and place him in a room with all these books described above. John sits in this room and recieves prompts in Chinese. He follows the rules of the books and produces an output in Chinese. John doesn’t know Chinese himself, but he fools any speaker/reader into believing he does. The question is: is this truly a demenstration of “intelligence” in Chinese? John says no.
It should be restated that the original computer program could pass a Turing Test in Chinese, so it stands to reason that John can also pass such a test using the Chinese Room. But John himself doesn’t know Chinese, so it’s ridiculous to say (says John) that passing this Turing Test demonstrates “intelligence.”
One natural response is to say that “the room as a whole” knows Chinese, but John pushed back against this. The Chinese Room only has instructions in it, it cannot take action on its own, therefore it cannot be said to “know” anything. John doesn’t know Chinese, and only follows written instructions, the room doesn’t know Chinese, in fact it doesn’t “know” anything. Two things which don’t know Chinese cannot add up to one thing that does, right?
But here is where John and I differ, because while I’m certainly not the first one to argue so, I would say that the real answer to the Chinese Room problem is either that “yes, the room does know Chinese” or “it is impossible to define what “knowing” even is.”

Let’s take John out of his Chinese Room and put him into a brain. Let’s shrink him down to the size of a neuron, and place him in a new room hooked up to many other neurons. John now receives chemical signals delivered from the neurons behind him. His new room has a new set of books which tell him what mathematical operations to perform based on those signals. And he uses that math to create new signals which he sends on to the neurons in front of him. In this way he can act like a neuron in the dense neural network that is the brain.
Now let’s say that our shrunken down John-neuron is actually in my brain, and he’s replaced one of my neurons. I actually do speak Chinese. And if John can process chemical signals as fast as a neuron can, I would be able to speak Chinese just as well as I can. Certainly we’d still say that John doesn’t speak Chinese, and it’s hard to argue that the room as a whole speaks Chinese (it’s just replacing a neuron after all). But I definitely speak Chinese, and I like to think I’m intelligent. So where then, does this intelligence come from?
In fact every single neuron in my brain could be replaced with a John-neuron, each one of which is now a room full of mathematical rules and functions, each one of which takes in a signal, does math, and gives an input to the neurons further down the line. And if al these John-neurons can act as fast as my neurons, they could all do the job of my brain, which contains all of my knowledge and intelligence, even though John himself (and his many rooms) know nothing about me.
Or instead each one of my neurons could be examined in detail and turned into a mathematical operation. “If you recieve these specific impulses, give this output.” A neuron can only take finitely many actions, and all the actions of a neuron can be defined purely mathematically (if we believe in realism).
Thus every single neuron of my brain could be represented mathematically, their actions forming a complete mathematical function, and yet again all these mathematical operations and functions could be written down on books to be placed in a room for John to sit in. Sitting in that room, John would be able to take in any input and respond to it just as I would, and that includes taking in Chinese inputs and responding in Chinese.

You may notice that I’m not really disproving John’s original premise of the Chinese Room, instead I’m just trying to point out an absurdity of it. It is difficult to even say where knowledge begins in the first place.
John asserts that the Chinese room is just books with instructions, it cannot be said to “know” anything. And so if John doesn’t know Chinese, and the Room doesn’t know Chinese, then you cannot say that John-plus-the-Room knows Chinese either, where does this knowledge come from?
But in the same sense none of my neurons “knows” anything, they are simply chemical instructions that respond to chemical inputs and create chemical outputs. Yet surely I can be said to “know” something? At the very least (as Decarte once said) can’t I Know that I Am?
And replacing any neuron with a little machine doing a neuron’s job doesn’t change anything, the neural net of my brain still works so long as the neuron (from the outside) is fundementally indistinguishable from a “real” neuron, just as John’s Chinese Room (from the outside) is fundementally indistinguishable from a “real” knower of Chinese.
So how do many things that don’t know anything sum up to something that does? John’s Chinese Room is really just asking this very question. John doesn’t have an answer to this question, and neither do I. But because John can’t answer the question, he decides that the answer is “it doesn’t,” and I don’t agree with that.
When I first heard about the Chinese room my answer was that “obviously John *can’t* fool people into thinking he knows Chinese, if he has to do all that math and calculations to produce an output, then any speaker will realize that he isn’t answering fast enough to actually be fluent.” My teacher responded that we should assume John can do the math and stuff arbitrarily fast. But that answer really just brings me back to my little idea about neurons from above, if John can do stuff arbitrarily fast, then he could also take on the job of any neuron using a set of rules just as he could take on the job of a Chinese-knower.
And so really the question just comes back to “where does knowledge begin.” It’s an interesting question to raise, but raising the question doesn’t provide an answer. John tries at a proof-by-contradiction by saying that the Room and John don’t know Chinese individually, so you cannot say that together they know Chinese. I respond by saying that none of my individual neurons know Chinese, yet taken together they (meaning “I”) do indeed know Chinese. I don’t agree that he’s created an actual contradiction here, so I don’t agree with his conclusion.

I don’t know where knowledge comes from, but I disagree with John that his Chinese Room thought experiment disproves the idea that “knowledge” underlies the Turing Test. Maybe John is right and the Turing Test isn’t useful, but he needs more than the Chinese Room to prove that.
Ultimately this post has been a huge waste of time, like any good philosophy. But I think wasting time is sometimes important and I hope you’d had as much fun reading this as I had writing it. Until next time.