Sir Keir Starmer, the newly elected King of England, 2024 pencil sketch
Last time on Streams of Consciousness, I was talking about the economy of Great Britain and what they needed to change to improve things. They’ve tried raising taxes, they’ve tried cutting spending, but their fiscal deficit is only rising and new loans to cover the deficit are getting ever more expensive. My previous recommendation was spicy and probably unpopular, so I quarantined it in its own post and am putting the rest of my recommendations here.
But first: what should Great Britain *not* do? Well first of all I agree with Tony Blair: they shouldn’t put retaliatory tariffs on America. And this isn’t because I’m biased and don’t want them to hurt America, it’s because *I want what’s best for Britain and don’t want them to hurt themselves*.
It may sting to allow Donald Trump a “win.” He’s jacked up tariffs and demanded that no one else retaliates with their own. If you do what he’s asking, aren’t you letting him win? Well if you think retaliatory tariffs are a smart move, you must think that because you believe they will hurt America with only a modest affect on your own country. But that’s wrong, tariffs are a huge blow to your own country, with only a modest affect on the one you’re tariffing. Doing what Donald Trump wants just means letting him win the foot-shooting competition.
Tariffs are inflation in action: everything gets more expensive for absolutely no reason. Because everything is more expensive, everyone is poorer (since their money doesn’t go as far). And tariffs don’t “protect” domestic industries, they destroy them. They destroy competitiveness because there is no market force pushing companies to improve their products. With tariffs, it’s always more viable to increase your profits by rent seeking (demanding the tariffs rise yet further) rather than by self-improvement. Thus the companies stagnate and rust out. Less goods are produced at a much higher cost, everyone is poorer.
This is true even when your tariffs are “targeted.” It’s just that “targeted” tariffs destroy only a few industries instead of all of them. Donald Trump tariffed you, but if you retaliate with tariffs on on American fuel and aircraft (major American exports), you’ll harm your own airline industry by raising their costs. Needless to say your airlines will have to raise their own costs, harming your tourism/travel industries, and thereby harming your citizens who can no longer afford airfares. America will feel some harm, yes, but not as much as your own people.
“We’ll substitute American goods by buying goods from Europe!” Trump wants to substitute foreign goods with American goods, do you think that will work for him? It won’t work for you either.
Tariffs also destroy industries by raising the cost of all their inputs, since again tariffs are just inflation. The steel company can raise its prices since it’s no longer competing with Chinese steel, and has no incentive to innovate because it plans to ask for more tariffs next year. So if you’re a manufacturing company making anything with steel, all your steel just got very expensive and will only get more expensive from here. Might as well cut wages, it’s the only cost you can control.
Many manufacturers will go bankrupt, they can’t afford the higher prices. A few dozen steel jobs will be “saved” at the cost of thousands of higher-paying manfacturing jobs. Those steel workers will then be laid off because with all the manufacturers going bankrupt, no one needs so much steel. And besides, the cost of iron has gone up with the tariffs on iron (and the iron mine is soon to go bankrupt as they can’t afford the machines needed to keep mining).
Think of it this way: if you think retaliatory tariffs are a good idea, then you think Trump’s tariffs in general are a good idea. You agree with him that the tariffs hurt the target countries more than they hurt the country placing them. You think Trump is doing smart economic policy, and are just mad that he’s doing it to *you*.
So again, don’t complain about giving Trump a *win*, reject the cognitive dissonance on tariffs and accept the one and only truth: tariffs are bad for growth, bad for prices, and bad for workers. Biden knew this in 2019, but I fear the cognitive decline hit him fast since he forgot it by 2021. (example, example, example)

Anyway that’s what Britain *shouldn’t* do, so what *should* it do?
How about reducing the need for occupational licensing? “Licensing” sounds good in theory, the Government is going to step in and demand minimum qualifications for certain professions. But everything sounds good when you ignore the costs and handwave the benefits.
Licensing sounds nice because you immediately think of doctors and nurses. But many many jobs have mandatory licenses that simply do not need them. Does a horse trainer really need a license? A piano tuner? A wig-maker? Adding a license does nothing except make it harder for people to get jobs. It’s part of what’s killed “entry-level” positions, there is no such thing as “entry-level” in an industry where any work at all requires a specific license.
20% of UK jobs need a specific license, which ossifies the labor marker and prevents workers from job-hopping to find better wages. You may have veterinary training, a fondness for horses, and see well-paying jobs opening up in the horse-racing industry. But without a long and arduous licensing process, you’re cut out from that part of the labor market, forced to keep working at Tesco for almost nothing.
You may ask “but without a license, how can we ensure these workers are competent?” You interview them, you look at their CV, you contact prior employers. An incompetent employee can do damage yes, for instance an incompetent Tesco stocker can leave heavy merchandise off-balance to crush unwary shoppers, so do shelf stockers need a license? Be honest, exactly how much is saved by having entry-level jobs be licensed? Quantify all the harms, both physical and monetary, then weigh them up against the costs.
Because licensing *does* have a cost. It lowers social mobility since the lower class can’t afford to spend years getting licensed before getting their first job. It hampers growth by preventing industries from growing to meet demand. And it drastically raises costs for licensed labor, without really raising wages.
How can that be? Aren’t licensed jobs paid more than unlicensed? Yes but look at the cost of getting that license, with its years of training and bureaucracy. Look at the cost of *keeping* that license, with mandatory retraining, continuing education, and the like. Time is money, and all the time it takes getting and keeping a license usually drains any additional pay that the license brings.
And look at how that license locks you into a single career, unable to switch things up to chase a higher wage. I’m sorry, you’re a *horse* trainer, *dog* training is a different license.
And study after study shows that very few licenses improve outcomes. Doctor, nurse, these require years of training and understudy, a license here may be warranted. But this kind of thinking is needlessly applied to far too many jobs, most of which show no difference in quality between licensed professionals (in countries where a license is needed), and unlicensed professionals (in countries where it isn’t). License medical and legal practitioners, let everyone else be.
So that’s occupational licensing. My next suggestion for Keir: end planning permission and build housing on the green belt. I wrote about the Green Belt before, but for those of you who missed it: the Green Belt isn’t green, and Britain should build on it.
“The Green belt” of is a bunch of land surrounding many of Britain’s largest cities. The name conjures to mind beautiful forests and fields, untouched by Man since the days of yore. But it’s actually car parks and monoculture farms, forbidden from being built on so that landowners can prevent their neighbor’s property from being bought up by the urban bourgeoisie. It’s a NIMBY version of feudalism.
And the Green Belt does have houses by the way. NIMBY houses for people who don’t want anyone to live near them, but also don’t want to pay for that privilege. Instead of buying the land surrounding their house (and thus paying tax on it), they simply demand no one *else* be allowed to build anything there.
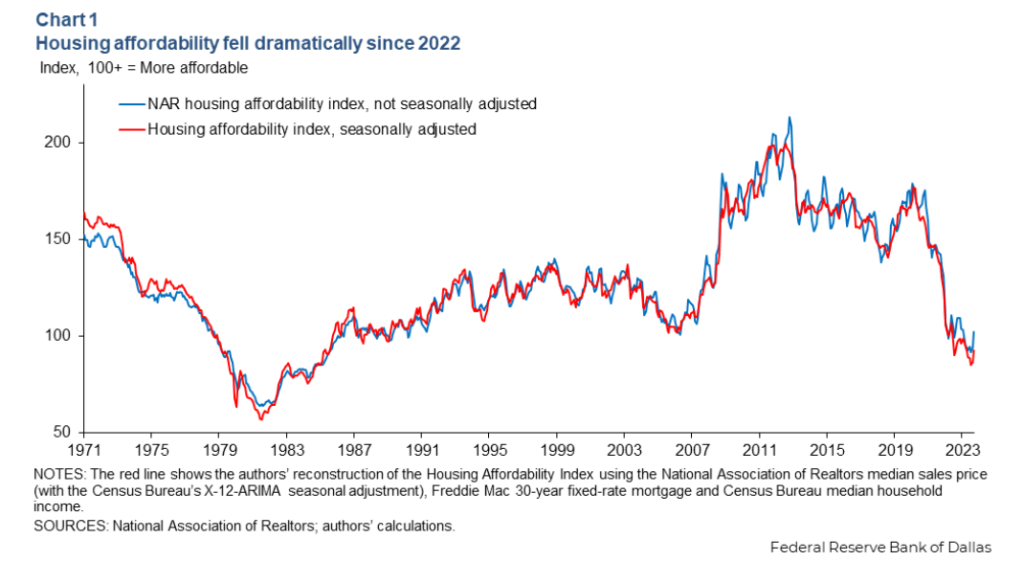
So build on the Green Belt, put apartments on the car parks. Housing is unaffordable in Britain, build more houses and prices will come down. Build more apartments and rent will come down. And with housing and rent getting cheaper, people can afford to spend more on buying goods and services, pumping more money into the economy and creating more jobs.
Importantly, *the Government does not need to do this building*. Too many people think that if the Government is not actively building things, either with its own taxpayer-funded corporation or through special subsidies, then things just won’t get built. But that is not at all true. A plethora of private companies would love to build and sell houses, but Government laws prevent them. So just repeal the laws and the companies will build, no special subsidies or taxpayer-funded company necessary.
And while we’re at it, do away with local planning permission. People complain about developers “banking” land, holding it without building for years. That’s only done because it takes on average a *decade* to get permission to build anything. If someone wants to build and sell houses, buying the land is step 1, steps 2-90 are all planning permission. Cut out those steps and the houses will be built faster and cheaper.
Local councils hold far too much power to block housing, get rid of that power. Instead of a situation where council have to give “permission,” create a national “by-right” system of planning. Developers submit a proposal to build a dwelling at a location, a national organization makes sure it’s up to code, and once they OK it development starts. No more veto-ocracy by local NIMBYs.
Great Britain is no longer a feudal society, you shouldn’t require the permission of the local landlords to build on your own land. Local landlords don’t want you to build a nice apartment that competes with their crack house? Tough. End local planning permission and kick the landlords to the curb.
And now here’s my final suggestion for Keir Starmer, get rid of bank ring-fencing.
Actually that’s not my suggestion, but it was raised as a possibility by British politicians. And the suggestion isn’t that outlandish, Germany ended its ring-fencing over a decade ago
But wait, what is/was ring-fencing? In 2008, the Financial Crisis/Great Recession happened when banks made risky loans, those loans defaulted, and the banks went bust. This cause a knock-on effect throughout the economy.
The risky loans often came from the “investment” side of the banking business, but when the bank went bust even the the “core” side (which held consumer’s money) was hit. Ring-fencing meant keeping investment banking separate from consumer banking, so any bad investment bets would have no effect on consumer savings.
But banks are banks, and economies of scale mean one bank doing two things is usually more efficient than two separate banks. That’s why some want to get rid of ring-fencing and let banks make more money. Germany already did so, why shouldn’t Great Britain? Let the good times roll again.
I don’t know if ending ring-fencing is good or not because honestly I don’t actually know much about its effect. What efficiency is gained by combining consumer banking and investment banking? What is lost by ring-fencing? But I don’t reflexively hate this idea the way I probably would have hated it 10 years ago, less than a decade after the Financial Crisis. I don’t know, I’ll need to do more reading.
So anyway those are my proposals the economy of Great Britain. Keir, if you’re reading: work on this for me, would you?
Deregulation is a dirty word on the left mostly because it’s a clean word on the right. But this reflexive partisanship isn’t helpful, regulations are not always good. Removing bad ones is necessary for an economy to grow. And if Labour wants growth, if they want to stop having to come out with more taxes and less spending every six months, then they need deregulation.
Post Script: Talking about the banking deregulation, I was reminded of Thatcher’s “Financial Big Bang.” No time to discuss it today, but I hope I remember to do so soon, because it’s a fascinating topic that explains a lot about today’s Great Britain.